The prevalence of King Charles III’s admission to a private hospital for a procedure to address an enlarged prostate has ignited interest in a condition that is exceedingly common among older men.
This occurrence has brought to light the significance of understanding and addressing benign prostatic hyperplasia, shedding light on a condition that impacts a substantial portion of the male population as they age.
The 75-year-old monarch’s situation is emblematic of a widespread issue, as statistics indicate that approximately half of men in their 50s experience an enlarged prostate, a figure that escalates to over 80% among men by the time they reach the age of 80.
As Dr. Stephen Nakada, a distinguished urologist at the University of Wisconsin, aptly notes, an enlarged prostate is a common consequence of aging, akin to the emergence of gray hair.
While an enlarged prostate may not always manifest noticeable symptoms, when it does, the resulting effects can be bothersome, varying in intensity among individuals.
Understanding the nature of this condition, also referred to as benign prostatic hyperplasia, is pivotal in comprehending its impact and addressing the concerns associated with it.
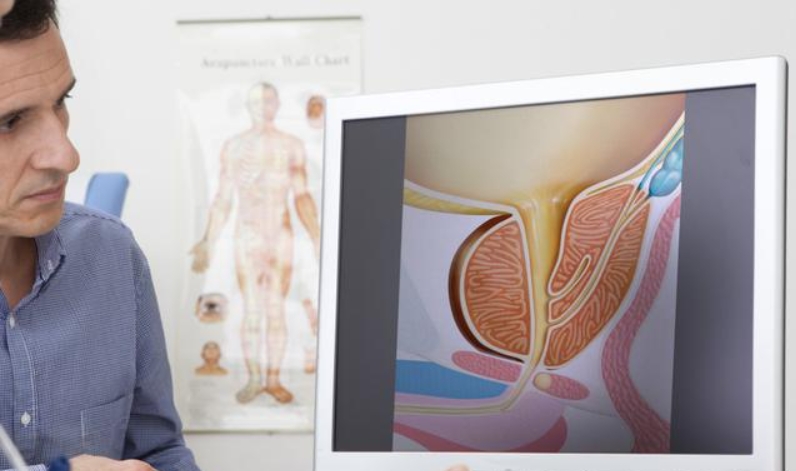
To truly comprehend the implications of an enlarged prostate, it is essential to delve into the intricacies of the prostate gland itself.
The prostate, an integral component of the male reproductive system, plays a vital role in the production of seminal fluid.
Situated beneath the bladder, it envelops the urethra, the conduit responsible for the passage of urine and semen through the penis.
This intricate positioning underscores the potential impact of an enlarged prostate on urinary and reproductive functions, necessitating a comprehensive understanding of its causes and symptoms.
Contrary to common misconceptions, an enlarged prostate, also known as benign prostatic hyperplasia, is not indicative of cancer.
The term “benign” in this context explicitly denotes the non-cancerous nature of the condition. The precise factors contributing to prostate enlargement remain somewhat elusive, with hormonal fluctuations emerging as a potential catalyst for this physiological transformation as men progress in age.
The manifestation of an enlarged prostate often presents a spectrum of symptoms that can significantly disrupt an individual’s daily routine.
These symptoms may encompass increased frequency of urination, particularly during the night, coupled with difficulties in initiating urination and experiencing post-void dribbling.
Additionally, the inability to fully empty the bladder is a prevalent symptom that can significantly impact an individual’s quality of life.
The acknowledgment of the prevalence of an enlarged prostate among older men, exemplified by the recent news concerning King Charles III, underscores the importance of raising awareness about this condition.
By fostering a deeper understanding of benign prostatic hyperplasia, it becomes possible to develop more effective strategies for its management and treatment.
Furthermore, the emphasis on education and awareness serves to empower individuals and healthcare professionals alike in addressing the multifaceted challenges posed by an enlarged prostate.
In conclusion, the announcement of King Charles III’s hospital admission for an enlarged prostate procedure has brought to the forefront a condition that affects a substantial portion of the male population as they age.
Understanding the intricacies of benign prostatic hyperplasia, including its causes and symptoms, is pivotal in fostering a more comprehensive approach to addressing this prevalent condition.
By elevating awareness and knowledge surrounding an enlarged prostate, we can strive to enhance the quality of care and support available to those affected by this common age-related ailment.
In the realm of addressing symptoms related to an enlarged prostate, medical professionals often recommend initial lifestyle adjustments such as limiting fluid intake after dinner and reducing the consumption of substances known to exacerbate symptoms, such as alcohol, caffeine, and spicy foods.
Dr. Nakada emphasized the potential benefits of decreasing caffeine and alcohol intake, citing their potential to irritate the bladder.
When it comes to diagnosis, doctors typically inquire about symptoms and medications, and conduct a rectal exam to assess the size and shape of the prostate.
Treatment options include medications that relax muscles to facilitate improved urine flow, as well as drugs that can impede prostate growth.
In some cases, erectile dysfunction medications may also aid in urine flow. While herbal remedies like saw palmetto are commonly sought, Dr. Nakada expressed reservations about their efficacy, often advising patients against their use.
Surgical interventions, ranging from tissue removal to urethral widening, are available, employing techniques such as laser pulses, microwaves, ultrasound, electric currents, heated water, and stent insertion.
It is important to note that all surgical procedures carry potential risks, including bleeding, infections, and the possibility of urinary or sexual complications. Additionally, less invasive procedures may require repetition if symptoms resurface.
In response to the original inquiry about the symptoms and treatment of an enlarged prostate, it’s important to consider various aspects that might help alleviate symptoms.
Medical professionals often recommend lifestyle adjustments, such as reducing fluid intake after dinner and minimizing the consumption of substances like alcohol and caffeine.
Additionally, certain medications, including antihistamines, can exacerbate symptoms and may need to be adjusted. Dr. Nakada suggests that modifying one’s diet by reducing the intake of spicy foods, caffeine, and alcohol can help alleviate bladder irritation, which is often associated with an enlarged prostate.
When it comes to diagnosing an enlarged prostate, doctors typically inquire about symptoms and current medications.
A rectal exam is commonly performed to assess the size and shape of the prostate. Furthermore, there are medications available that serve different purposes, including muscle relaxants to improve urine flow and drugs that can inhibit the growth of the prostate.
Erectile dysfunction medications have also been found to assist with urine flow. However, it’s important to note that herbal remedies like saw palmetto lack strong evidence for their efficacy in treating an enlarged prostate.
In cases where surgical intervention is necessary, there are various procedures aimed at removing prostate tissue or widening the urethra.
These techniques encompass the use of laser beams, microwaves, ultrasound, electric current, heated water, and stents to facilitate urine flow.
Surgical options also include techniques to excise tissue, each with its own set of potential complications, such as bleeding, infections, and urinary or sexual issues. In some instances, less invasive procedures may need to be repeated if symptoms reappear.
In summary, the symptoms of an enlarged prostate can be managed through a combination of lifestyle adjustments, medications, and surgical interventions.
It’s important for individuals to consult with healthcare professionals to determine the most suitable treatment plan based on their specific circumstances and medical history.
